News
How Modern Energy Storage Systems Are Designed: From Grid-Forming Control to Multi-Value Applications
- January 20, 2026

Why Energy Storage System Design Is No Longer Simple
Energy storage has evolved from a backup-only solution into a core asset of the modern power grid. Today, Energy Storage System Design must simultaneously address grid stability, renewable integration, power quality, and multiple value streams. As inverter-based resources replace synchronous generation, Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are increasingly expected to function as active grid infrastructure rather than passive devices.
In modern power grid environments with high PV penetration, design choices directly impact grid reliability, project economics, and battery lifespan—especially in PV + Energy Storage Integration and C&I Energy Storage Systems, where storage must support both on-site loads and grid interaction.
Core Architecture of Modern Energy Storage Systems
Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) as a System-Level Asset
A modern battery storage system comprises several elements. These include power control systems, a battery management system, protection devices, and communication networks. In addition, an energy management system is required. Finally, a battery pack is required. System integration at a comprehensive level is critical.
In-built BESS solutions allow project timelines to be met with lower on-site engineering risk and commissioning periods and also offer enhanced operational performance over the project’s lifetime particularly in installations which range from a few hundred kW to several MW.
AC-Coupled vs DC-Coupled Design Choices
Both AC-coupled and DC-coupled architectures are widely used in energy storage system design:
- DC-coupled systems offer higher efficiency for new PV + storage projects and enable tighter coordination between battery clusters and PCS.
- AC-coupled systems provide greater flexibility for retrofitting existing PV plants and allow independent scaling of PV and storage capacity.
The optimal choice depends on grid requirements, expansion plans, and control complexity.
Integrating BESS with PV Systems: The 800V Architecture
Where to Connect an 800V BESS in an 800V PV Collection Bus
The pursuit of higher energy density and lower system losses is the core driving force behind 800V design. In large-scale solar plants and advanced C&I projects, 800V / 800Vac architectures are becoming standard. Directly connecting an 800V BESS to an 800V PV collection bus minimizes transformer stages, reduces conversion losses, and simplifies system topology.
FFD POWER has deployed over 70 MWh of 800 Vac BESS in real-world projects, including installations in Ukraine. These systems integrate directly with existing 800V PV plants and support peak shaving, energy arbitrage, and grid interaction without additional step-up transformers.
Design Implications for PV Arbitrage and Self-Consumption
In regions with volatile electricity pricing or negative daytime tariffs, BESS designs must support fast charging during PV overgeneration and controlled discharge during peak pricing windows. EMS-driven scheduling becomes essential for maximizing value while protecting battery lifecycle.
Grid-Forming Control: A Critical Capability for Modern Grids
What Makes a BESS Grid-Forming
A grid-forming energy storage system can establish voltage and frequency autonomously, unlike grid-following inverters that rely on an existing grid signal. Grid-forming capability is achieved through advanced PCS control modes such as VSG (Virtual Synchronous Generator) and VF (Voltage-Frequency) control.
This capability is critical in weak grids, islanded microgrids, and blackout recovery scenarios.
Grid-Forming in Utility and C&I Applications
Grid-forming BESS enables black start, seamless islanding, and stable operation in low-inertia networks. Systems such as Galaxy 5015 support PQ, VF, and VSG modes, allowing operators to switch between grid-following and grid-forming behavior depending on operational needs.
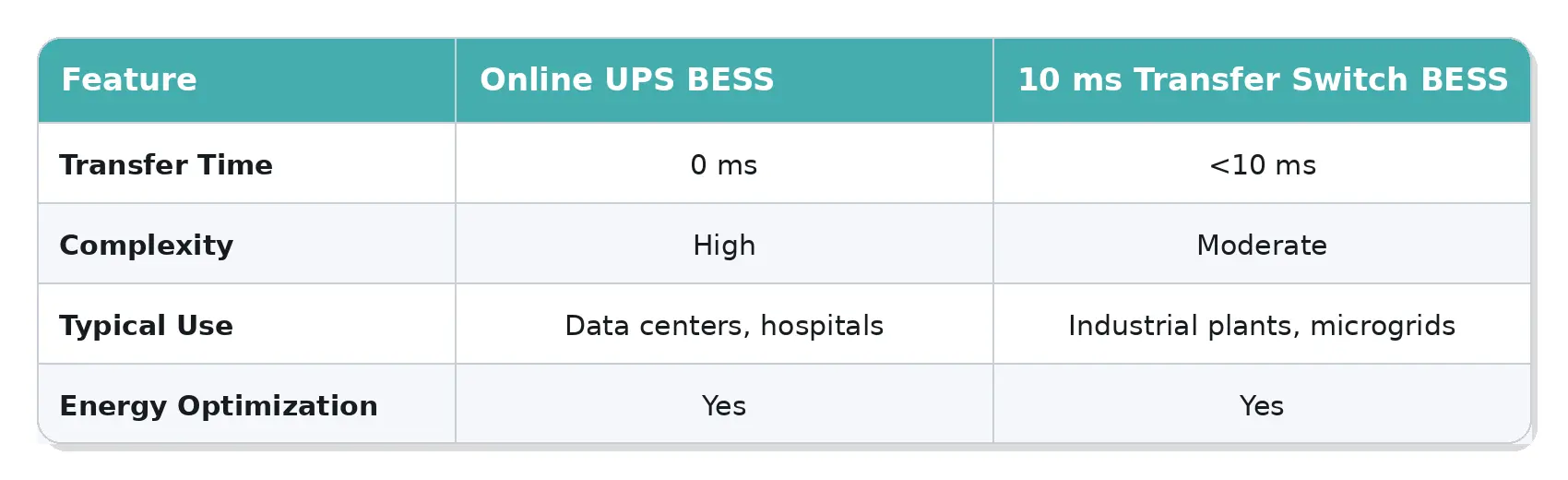
Power Continuity Design: Online UPS vs Seamless Transfer Switching
Online UPS-Based Energy Storage
Lithium battery online UPS systems use true double-conversion topology, providing zero transfer time and complete isolation from grid disturbances. These systems are ideal for data centers, hospitals, and mission-critical facilities where even millisecond interruptions are unacceptable.
10 ms Seamless Transfer Switch Solutions
For many industrial and microgrid applications, a <10 ms static transfer switch provides sufficient continuity. This approach reduces system complexity and cost while still protecting sensitive loads during grid events.
Multi-Value Applications: One System, Multiple Benefits
TOU Arbitrage and Load Shifting
One of the most common applications for C&I Energy Storage Systems is Time-of-Use (TOU) arbitrage. By charging during low-tariff periods and discharging during peak hours, BESS significantly reduces electricity costs.
Grid Frequency and Ancillary Services
Modern BESS can simultaneously participate in frequency regulation services such as FCR and aFRR while serving on-site loads. Fast-response PCS and low-latency EMS coordination enable this dual operation without compromising system reliability.
Behind-the-Meter Energy Storage for C&I Users
Behind-the-meter energy storage refers to systems installed on the customer side of the utility meter. These systems are controlled by the site owner and optimized for cost reduction, reliability, and energy independence.
Typical BTM applications include factories, commercial buildings, EV charging stations, and industrial campuses.
Sizing BESS for Peak Shaving
Peak shaving requires careful analysis of load profiles and demand charges. Oversizing power capacity increases effectiveness, while oversizing energy capacity increases cost. A balanced design is essential for long-term ROI.
The Role of Advanced BMS in Safety and Battery Life
An advanced Battery Management System (BMS) is central to safe and durable BESS operation. For example, FFD POWER’s BMS simplifies traditional three-level architectures into a two-level structure, reducing system complexity while improving responsiveness.
Key BMS functions include:
- Accurate SOC and SOH estimation
- Active balancing at cluster level
- Thermal runaway prevention
- Coordination with PCS during partial cluster operation
These features are especially critical in high-cycling C&I Energy Storage Systems.

Recommended Energy Storage System Suppliers
1.FFD POWER
- 800V PV + BESS Integration
FFD POWER’s 800 Vac BESS connects directly to 800V PV collection buses, reducing system losses and simplifying PV-plus-storage architecture.
- Power Continuity Options
The portfolio supports both zero-transfer-time online UPS-BESS and <10 ms seamless transfer switching, matching different critical-load requirements.
- Grid-Forming Control
With VSG and VF control modes, systems can operate in grid-forming mode to support voltage and frequency stability.
- Multi-Value Operation
A unified EMS enables TOU arbitrage and grid frequency services within one storage system.
- Behind-the-Meter Peak Shaving
For C&I BTM storage, sizing is based on load profiles to reduce peak demand charges.
- Advanced BMS Architecture
A two-level BMS improves safety, enables active balancing, and extends battery life in high-cycling applications
2.Sungrow
Sungrow provides utility-scale and C&I BESS solutions with strong PV + storage integration.
3.Tesla
Tesla’s Megapack is widely deployed in utility-scale energy storage projects. It emphasizes high energy density, and software-driven optimization for grid services and renewable integration.
4.Siemens
Siemens delivers grid-scale and industrial energy storage solutions focused on grid stability and digital control.
Conclusion
Modern energy storage is no longer about choosing batteries alone. Energy Storage System Design now integrates grid-forming control, PV coupling strategies, power continuity solutions, and multi-value operation into a unified architecture. Systems that balance flexibility, safety, and scalability will define the future of the modern power grid.
FAQ
Q: What is the main difference between grid-forming and grid-following energy storage?
A: Grid-forming systems can establish voltage and frequency independently, while grid-following systems rely on an existing grid reference.
Q: Is 800V BESS integration suitable for C&I projects?
A: Yes. 800V architectures reduce losses and simplify integration, especially in PV-heavy C&I systems.
Q: Can one BESS perform TOU arbitrage and frequency regulation at the same time?
A: Yes. With proper EMS control, a single system can stack multiple value streams.
Q: When should I choose an online UPS instead of a seamless transfer switch?
A: Online UPS is preferred for zero-interruption requirements such as data centers and hospitals.
Q: How does an advanced BMS extend battery life?
A: By ensuring accurate monitoring, active balancing, thermal control, and coordinated PCS interaction.
