800V Battery Energy Storage System 800VAC BESS
An 800V Battery Energy Storage System (800V BESS) is an advanced low-voltage energy storage architecture designed to align with modern 800V-class photovoltaic (PV) inverter platforms.
As PV systems increasingly adopt 800V AC outputs, deploying an 800V BESS enables higher power density, lower current, reduced losses, and simplified system integration.
FFD POWER provides commercial and industrial (C&I) 800V BESS solutions engineered for PV integration, microgrids, data centers, and grid-interactive energy storage applications.

Why 800V BESS Matters ?
PV Inverters Are Driving the Voltage Shift
PV Inverters Are Driving the Transition to 800V AC Architecture
The global photovoltaic (PV) industry is rapidly transitioning toward 800V-class AC architectures, particularly in modern string inverter platforms.
This shift is driven by the need for higher power density, improved system efficiency, and better compatibility with large-scale commercial and industrial PV installations.
Higher Voltage Enables Higher Power with Lower Current
Operating at higher AC voltage allows PV systems to deliver the same power output with significantly lower current.
Lower current reduces electrical losses, minimizes thermal stress on cables and switchgear, and improves overall system efficiency in high-power applications.
Limitations of 400V and 690V Energy Storage Systems
Energy storage systems operating at 400V or 690V face inherent limitations when deployed in MW-scale PV-integrated projects.
These limitations include oversized low-voltage switchgear, excessive current, higher thermal losses, and complex parallel feeder configurations.
How 800V BESS Aligns with Modern PV System Design ?
An 800V battery energy storage system (BESS) aligns directly with the voltage level of modern PV inverters, enabling seamless system integration.
By matching the PV AC voltage, 800V BESS enables a cleaner low-voltage system design with simplified infrastructure and improved operational reliability.
FFD POWER 800V Battery Energy Storage System Design
FFD POWER 800V BESS is typically an AC-coupled LV solution where battery racks (DC) connect to a PCS, and the PCS outputs at ~800Vac class into a PV collection bus, then steps up to MV through a transformer for grid connection.
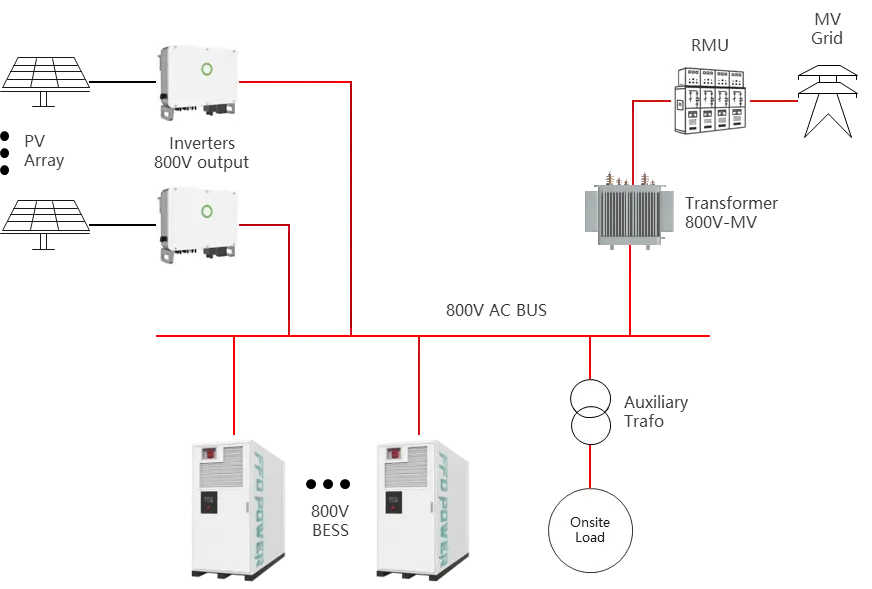
Battery System (DC)
LFP battery racks/packs, DC protection (fuses/contactors), insulation monitoring.
PCS (Power Conversion System)
Bidirectional inverter with grid-forming or grid-following capability or both (project-dependent).
EMS/SCADA
Dispatch, power factor/VAR control, peak shaving, PV self-consumption, backup modes, alarms, data logging.
LV AC Distribution (800V switchboard)
ACB/MCCB feeders, busbar, metering, protection relays, surge protection, earthing arrangement.
How 800V BESS works ?
Electrical Topology
The system adopts a high-voltage 800V AC bus architecture for efficient power distribution. PV inverters and the Power Conversion System (PCS) of the battery energy storage are connected to the main 800V bus through dedicated feeders. This design minimizes conversion losses, reduces cabling requirements, and ensures seamless integration between renewable generation and storage.
Dispatch Control Strategy
Our intelligent Energy Management System (EMS) centrally orchestrates power flow by issuing precise active (kW) and reactive (kVar) power setpoints to both PV inverters and the PCS. The control logic follows a clear priority stack to maximize self-consumption and economic benefits:
- Export excess PV generation to the grid
- Directly supply on-site loads with solar power
- Charge the battery using surplus PV energy
- Reserve battery capacity for critical backup and grid-support services
This optimized hierarchy ensures maximum utilization of renewable energy while maintaining system reliability.
Grid Interface and Power Exchange
The main step-up transformer connects the 800V bus to the medium-voltage (MV) grid, enabling bidirectional power flow for import and export. Operating limits are strictly governed by MV-side protection settings and local grid interconnection requirements, ensuring safe and compliant operation under all conditions.
Metering and Monitoring Boundaries
Accurate energy monitoring is achieved through dedicated metering points:
- PV generation output meter
- PCS (battery) input/output meter
- Main grid import/export meter
These boundaries provide precise data for billing, performance analysis, and regulatory compliance.
What’s special about FFD POWER 800V BESS Solution?

Utility-Grade 800V Performance, C&I Deployment Flexibility
FFD POWER’s 800V BESS Solution is built to deliver utility-grade performance with C&I-level deployment flexibility—making it a practical choice for microgrids, PV+storage, demanding off-grid sites, and grid balancing services. At the core is our string-type PCS architecture, designed to support multiple PCS units (up to 20) in off-grid parallel operation, enabling high power scalability, strong redundancy, and stable system expansion without a single-point bottleneck.
Siemens PLC-Based EMS With Deterministic PROFINET Control
FFD POWER’s 800V BESS Solution is built to deliver utility-grade performance with C&I-level deployment flexibility—making it a practical choice for microgrids, PV+storage, demanding off-grid sites, and grid balancing services. At the core is our string-type PCS architecture, designed to support multiple PCS units (up to 20) in off-grid parallel operation, enabling high power scalability, strong redundancy, and stable system expansion without a single-point bottleneck.
Unified Multi-Mode Operation Without Downtime
The EMS is engineered as a unified multi-function control platform, allowing seamless switching among operating modes such as FCR, peak shaving, and self-consumption optimization without hardware replacement or system downtime. Crucially, all core control logic runs locally inside the PLC, ensuring real-time performance and high reliability even under weak network conditions or cloud communication interruptions.
Cost-Optimized Economics with Hybrid-Ready Design
Most importantly, we emphasize cost control: the all-in-one cabinet solution is priced close to containerized utility-scale BESS, making it especially competitive in regions where container logistics are limited or site access is restrictive. Combined with EMS-ready control logic, hybrid operation (PV/grid/diesel), and safety-focused design, FFD POWER delivers an 800V BESS solution optimized for performance, scalability, and bankable project economics.
Modular Integration Options for Different Site Constraints
For different site constraints, we offer multiple integration paths. Our battery + PCS all-in-one cabinet modules enable fast transport, rapid installation, and step-by-step capacity expansion—ideal for projects that need modular growth. We also provide a PCS-split containerized design where PCS can be integrated into a dedicated container, with an option to directly integrate the transformer for MV interconnection, reducing on-site engineering scope and shortening commissioning time.
Certified for Global Deployment Readiness
FFD POWER’s 800V BESS Solution is designed for international project delivery and compliance alignment. Key certifications and documentation packages include IEC 62619, IEC 63056, CE-EMC, and UN transportation compliance support, alongside standard MSDS documentation—helping streamline qualification, logistics, and project acceptance across diverse markets.
Certified for Global Deployment Readiness
FFD POWER’s 800V BESS Solution is designed for international project delivery and compliance alignment. Key certifications and documentation packages include IEC 62619, IEC 63056, CE-EMC, and UN transportation compliance support, alongside standard MSDS documentation—helping streamline qualification, logistics, and project acceptance across diverse markets.
International Compliance and Cybersecurity Considerations
For international projects, this approach also reduces policy, compliance, and potential geopolitical risks by leveraging non-China industrial control components, aligning with European and global expectations around cybersecurity, system controllability, and long-term maintainability. Overall, the PLC-based EMS provides a future-ready software foundation that can rapidly adapt to changing market mechanisms and grid-service requirements.
400V vs 690V vs 800V BESS Solution: The Current Problem Is the Real Constraint
The biggest practical limitation of 400V systems at MW scale is not “voltage preference”—it is current.
For three-phase AC, current roughly scales as:
I ≈ P / (√3 × V × pf)
Assuming pf ≈ 1 for a quick comparison:
- 2 MW @ 400V → I ≈ 2,000,000 / (1.732×400) ≈ 2,886 A
- 2 MW @ 690V → I ≈ 2,000,000 / (1.732×690) ≈ 1,673 A
- 2 MW @ 800V → I ≈ 2,000,000 / (1.732×800) ≈ 1,443 A
What this means in real projects
- 400V quickly forces you into very large ACB ratings (e.g., 3200A+), thicker busbars, heavier copper, higher heat, and more engineering effort in short-circuit and selectivity studies.
- 690V improves the situation, but at higher MW levels you still face large currents and paralleling complexity.
- 800V further reduces current, which directly improves:
- cable size and routing,
- busbar thermal margin,
- switchgear stress and fault management,
- total feeder count for the same MW capacity.
If your solution targets MW-scale C&I (data centers, factories, PV plants, ports, industrial parks), the 800V architecture is a straightforward way to scale power without turning the LV room into a copper-and-ACB museum.
Transformer Selection: Where 400V/690V Often Becomes Painful
When exporting to MV, the LV side of the step-up transformer must handle the full power. At 400V, even a moderate transformer size implies very high LV current, which cascades into:
- oversized LV switchboards,
- more parallel LV runs,
- higher losses and temperature rise,
- higher fault current contribution management complexity.
Why 800V helps: With lower LV current for the same MW, your transformer LV side, LV switchgear, and cabling become more manageable. This reduces installation complexity and can improve both schedule and reliability.
In MW-scale systems, transformer LV current is the hidden constraint. 800V reduces LV current materially compared with 400V, enabling cleaner LV design and smoother MV interconnection.
While 690V also reduces current compared with 400V, the industry trajectory—particularly for next-generation string PV inverters—is increasingly aligned around 800V-class AC output. As a result, investing in a 690V architecture is becoming less compelling than moving directly to 800V, which better matches inverter roadmaps and supports a more consistent, future-proof system design.
The 800V Solution Advantage
- Higher Power Density at LV
Fewer feeders and lower current enable higher MW capacity per LV lineup and per container/shelter footprint. - Lower Losses and Better Thermal Margin
Lower current reduces I²R losses across busbars and cables, improving efficiency and reducing thermal stress over long operating hours. - Easier Engineering for MW-Scale Integration
Protection coordination, selectivity, cable routing, and expansion planning are more straightforward when current is not the dominating constraint. - Seamless 800V PV + BESS Integration (Transformer-Free at the LV Interface)
When PV inverters deliver an 800V-class AC output, an 800V BESS can couple to the same 800V collection bus with a cleaner electrical interface—often avoiding an additional “voltage-matching” LV transformer on the storage side. This simplifies the one-line design, reduces equipment count and footprint, shortens installation/commissioning work, and improves overall project economics by lowering capex and integration complexity. - Better Fit for PV + Storage Dispatch
An 800V battery energy storage system pairs naturally with higher-power PV blocks and can support:
- PV smoothing and ramp-rate control,
- peak shaving and demand charge management,
- TOU arbitrage (where applicable),
- backup power (with ATS/STS as required),
- grid support (Volt/VAR, frequency response) where permitted by the PCS capability and local grid code.

